Free printable and online worksheets to help Grade 6 students review how to construct and interpret a frequency histogram.
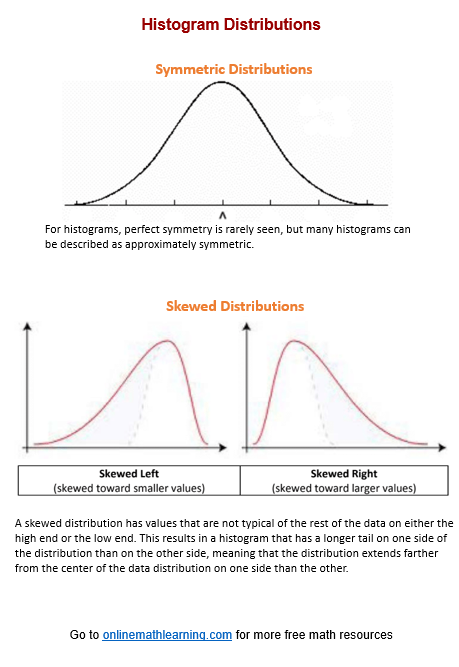
Histograms provide a visual representation of the distribution of a dataset. A histogram is useful to describe the shape of the data distribution. It is important to think about the shape of a data distribution because depending on the shape, there are different ways to describe important features of the distribution, such as center, variability, skewness, modality, and the presence of outliers. A histogram may have a symmetric or approximately symmetric distribution or it may have a skewed distribution.
Steps to Create a Histogram

Interpreting Histograms Distributions
Shape of Distribution:
Symmetrical: The left and right sides are approximately mirror images.
Skewed Left (Negative Skew): The left tail is longer; most data points are on the right.
Skewed Right (Positive Skew): The right tail is longer; most data points are on the left.
Modality:
Unimodal: One peak.
Bimodal: Two peaks.
Multimodal: More than two peaks.
Spread and Range:
Indicates the variability of the data.
Wide spread suggests high variability; narrow spread suggests low variability.
Outliers:
Data points that fall far outside the range of most other points.
Can be identified as isolated bars at either end of the histogram.
Click on the following worksheet to get a printable pdf document.
Scroll down the page for more Histogram Worksheets.


Try the free Mathway calculator and problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.
We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.